The main function of above-ground pipeline detectors is to detect underground pipelines in cities, such as gas, electricity, telecommunications, tap water, industrial pipelines, drainage, and cable television.
1. Working principle and method of underground pipeline detector The principle of electromagnetic induction is used to detect the precise orientation and depth of underground cables, as well as the open circuit, short circuit and failure points of the positioning cables. The intelligent full-character Chinese characters, graphic operation instructions and sound of the pipeline locator The FM indication makes it the easiest-to-use pipeline locator in use today. The built-in ohmmeter of the transmitter can automatically measure the loop resistance and continuous automatic output impedance matching to ensure the output of the matching signal. For the test of cable faults, the instrument can be used step voltage method, with the direct buried cable fault test accessories ("A") to determine the cable ground fault resistance and cable sheathing of the buried cable insulation resistance is less than 2M Europe The location of the fault; can also use the signal strength and weakness to determine the open circuit, short circuit fault. Using the coupling clamp, you can find the path of the live cable, use the 50Hz detection function of the receiver, and you can also track the 50Hz power frequency signal sent by the running cable, so that you can truly use one machine for multiple purposes and have a cost performance ratio.
Its basic working principle is: electromagnetic signals are generated by the transmitter, and the signal is transmitted to the underground cable under test through different transmission connection modes. After the underground cable senses the electromagnetic signal, an induced current is generated on the cable, and the induced current flows along the cable. Distant propagation, during the propagation of current, radiates electromagnetic waves through the underground cable to the ground. When the pipeline locator receiver detects the ground, it will receive an electromagnetic wave signal on the ground above the cable. The strength and weakness of the signal to determine the position and orientation of the underground cable and the working principle of the fault transmitter The signal transmission connection method of the transmitter: direct connection method, coupling method, induction method II. working principle of the underground pipeline detector receiver Method Three operating modes of the receiver: crest method, wave trough method, step voltage method.
(1) Crest method: When the detector receiver is located directly above the pipeline, the signal indicates the largest and the sound is the largest. Pay attention to adjusting the gain so that it can only detect the signal above or near the pipeline. The crest method uses the horizontal coil to receive the intensity of the horizontal component of the electromagnetic field, and performs peak detection on the interference-free cable. Directly above the cable, when the front of the receiver is perpendicular to the direction of the cable, the magnetic field response is at its maximum, not only because the coil is closest to the cable, but also because the magnetic field of the coil is strong, and because the magnetic flux of the magnetic field passes through the receiving coil at this time. When the receiver moves toward the sides of the cable, the intensity of the magnetic response on both sides is symmetrical and gradually decreases. This is not only because the coil is far away from the cable at this time, the magnetic field received by the receiver coil becomes weaker, but also because the direction of the magnetic field lines of the magnetic field is no longer perpendicular to the plane of the coil, and the magnetic flux passing through the coil becomes smaller, resulting in a peak like a mountain. The signal response. This is called the "peak method." 
(2) Valley method: When the detector receiver is located directly above the cable, the signal indication is minimal, and the receiver sound indication does not indicate any sound. Pay attention to adjust the gain so that the receiver has no signal and sound indication directly above the cable, and there is sound on both sides of the line. The wave trough method uses vertical coils to measure the vertical component of the electromagnetic field. The magnetic field on the target cable is composed of numerous circular magnetic lines concentric to the cable. The receiver has a minimum signal response right above the cable and a peak on both sides. This is due to the fact that the vertical component of the magnetic flux directly across the vertical receiving coil of the receiver is zero, when the magnetic flux through the vertical coil of the receiver is zero, the signal response has a minimum value (zero or minimum); When the receiver moves on both sides of the cable, the response of the instrument gradually increases as the receiver moves away from the cable. This is because the direction of the magnetic field lines at this time has formed a certain angle with the vertical coil plane of the receiver through the receiver. The magnetic flux of the coil gradually becomes larger. At the same time, as the receiver coil is farther away from the underground cable, the strength of the magnetic field detected by the receiver gradually weakens. When this factor becomes the main factor affecting the flux change through the coil, the response of the instrument will gradually become smaller, resulting in such as The same signal response in the valley. So called "valley method" 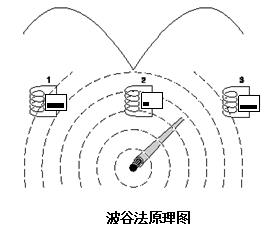
(3) Step voltage method: Through the "A" frame, it can detect the failure of the buried cable to the ground and the failure of the skin.
Connect the “A†frame to the receiver. The receiver can detect the leakage signal from the point of failure sent by the transmitter by receiving the “A†frame, which can easily locate the failure of the buried cable to the ground and the skin.
The accurate positioning of buried cable faults is particularly suitable for the fast and accurate positioning of insulation faults in street lamps, buried power cables, buried telecommunication cables, and buried optical cables. In particular, it is very useful for dead grounding of buried cables. When testing with traditional high-voltage flashover methods, the discharge energy of a single-phase metallic ground fault point is proportional to the square of the discharge current and the grounding resistance, and the grounding resistance is small, so the fault Click to wear gap discharge sound is lighter, can not be precise, or even fixed point.
Dear Customer:
Thank you for your attention to our products. In addition to this product introduction, the company also has transformer oil vacuum oil filter, mine stray current measuring instrument, high voltage short-circuit grounding wire, series resonance withstand voltage test device, silicone rubber high voltage wire, high voltage Rubber insulation mats and so on, if you are interested in our products, welcome to inquire. Thank you!
Tower Crane cabin is the control center of the crane and is attached to the slewing unit. In order to get to the tower crane cab, the operator must climb a series of ladders within the mast.
The movement of the tower crane is controlled from the operator`s cabin. Within the tower crane cabin, you`ll find the operator`s chair with joystick controller, electronic monitoring devices, and communication systems. Many cabins come with climate control to ensure a comfortable work environment. The Operator Cabin for Tower Crane is part of the slewing assembly.
Tower Crane Cab,Tower Crane Cabin Chair,Tower Crane Operator Cabin, Operator Cabin for Tower Crane,Spare Parts Cabin
SHEN YANG BAOQUAN BUSINESS CO., LTD , https://www.syconstructionhoist.com