Some friends often mention the switch networking method. This problem is really common. We have discussed it before. Some people often ask about 200-channel monitoring, how to choose a switch, how to network, etc., so let’s get to know this content today. .
First, small network
The access users are around 100 for small business networks. For this small network, our networking solution is:
In this scheme, each office is divided into independent vlans and a separate subnet is set up. The Layer 2 switch is used for the access layer, and the medium-sized Layer 3 switch is used as the core switching device to forward data between the subnets. The firewall runs after conversion and connects to the Internet;
Each Layer 2 switch accesses 12 or so users, and each interface of the medium-sized Layer 3 switch is set to a different vlan. The purpose of this is to prevent data between offices from interfering with each other. It also increases the speed of Internet access in each office; the data between each office is forwarded through the medium-sized Layer 3 switch for Layer 3, because the wire-speed forwarding performance of the switch, the data exchange between offices will not be lost. Package phenomenon.
The Layer 2 switch in the above figure recommends using a switch with 16 100M Ethernet interfaces or more. Of course, if the monitoring camera has a high bit rate, the 100M switch is not recommended.
There is no device at the aggregation layer in this networking solution, because the size of the network is too small, it is not necessary.
Second, medium-sized enterprise network
We refer to the enterprise network with the access user size of 300-800 as the small and medium-sized enterprise network. Once the network is large, it is difficult to manage, and the small network networking method of the principle cannot be used. For such a network, The following networking methods are available:
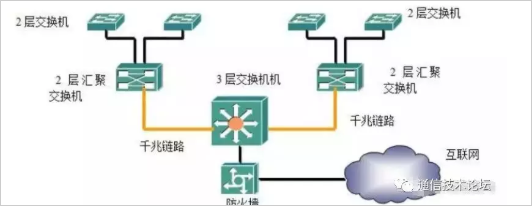
As the number of users in the network increases, we still use Layer 2 switches as pure access devices, and a device (2-layer aggregation switch) is added to the aggregation for aggregation.
Here we complement the role of the convergence layer:
The aggregation layer is the convergence point of multiple access layer switches. It must be able to handle all traffic from the access layer devices and provide uplinks to the core layer. Therefore, the aggregation layer switch needs to be compared with the access layer switch. Higher performance, fewer interfaces and higher switching rates.
The basic functions that the convergence layer mainly undertakes are:
1. Converging user traffic of the access layer to perform aggregation, forwarding, and exchange of data packet transmission;
2. Perform local routing, filtering, traffic balancing, QoS priority management, security mechanisms, IP address translation, traffic shaping, and multicast management according to the user traffic of the access layer.
3. Forward user traffic to the core switching layer or perform local routing processing according to the processing result;
4. Complete the conversion of various protocols (such as summary and re-release of routes) to ensure that the core layer is connected to the area where different protocols are running.
Gigabit lines are connected between the Layer 2 aggregation switch and the Layer 3 switch. This avoids the increase in the number of devices passing through the network, so as not to cause large delays in data exchange in the network.
A Layer 2 aggregation switch should have a multitude of 100M Ethernet interfaces (which can aggregate multiple Layer 2 switches) and multiple Gigabit Ethernet interfaces (providing high-speed uplink capability). The switch should support full line rate forwarding, support IEEE802.1q, port aggregation (Trunk), port rate control, priority queue management and other functions to meet the special requirements of various access scenarios.
Compared with the medium-sized network solution of the small enterprise network, it can be seen that the network only adds a few Layer 2 switches of the aggregation layer and several switches of the access layer. The previous devices can still be used, so the cost of network upgrade Relatively not high. In an actual enterprise, the enterprise network needs to be re-planned as the number of users increases, so this upgrade method is used more.
Third, medium and large enterprise networks
For enterprise networks with more than 1000 users but less than 3000, our networking solution is:
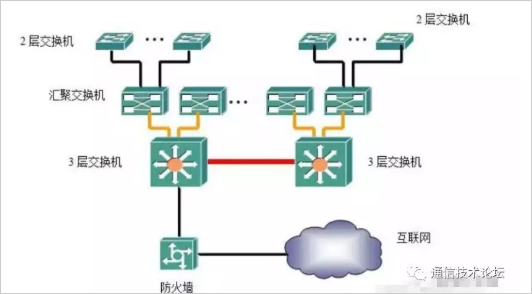
First of all, look at this network topology diagram is a bit complicated, but careful analysis is also the same as the above medium-sized network principle. With the further expansion of the network scale, using only one Layer 3 switch as the network core exchange may reduce the network processing performance. If the pressure is too high, there will be some problems of insufficient resources.
Fourth, large network networking
If the number of users exceeds 5000, we will locate it as a large enterprise network. For such a network, our networking solution is:
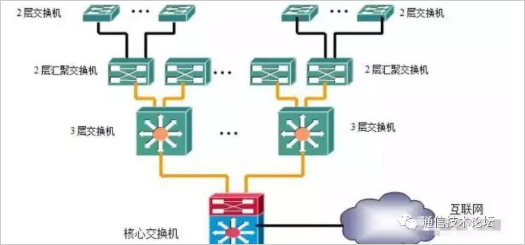
First we can analyze this topology map and add some switches.
For such a large-scale network, if multiple (such as more than 4) Layer 3 switches are used as the core equipment, it will increase the delay of network data exchange (maybe some data needs to go through all Layer 3 switches, and then count The delay of the Layer 2 access switch and the Layer 2 aggregation switch will cause the data forwarding delay to be too large, resulting in a decrease in network speed.
Therefore, large switching devices (core switches or core routers) need to be introduced to reduce the number of data passing devices.
Automatic Flip Platform Waterjet
Water Jet Table,Crossfire Cnc Plasma Table,Portable Cnc Plasma Cutter,Table Top Laser Cutting Machine
FOSHAN YUANLI PRECISION MACHINERY CO.,LTD , https://www.ylwaterjet.com